路由 (Router)
單頁應用程式 (SPA) 中的路由器處理根據 URL 顯示不同的頁面。與點擊連結時請求不同的遠端資源的預設行為不同,路由器會在本機設定 URL 以指向應用程式中的有效路由。然後,路由器偵測到此變更並決定要渲染的內容。
Yew 在 yew-router crate 中提供了路由器支援。要開始使用它,請將依賴項新增至您的 Cargo.toml 檔案中。
yew-router = { git = "https://github.com/yewstack/yew.git" }
所需的工具均在 yew_router::prelude 模組中提供,
用法
最開始,你需要定義一個 Route。
路由由一個 enum 定義,它衍生自 Routable。這個枚舉必須實作 Clone + PartialEq。
use yew_router::prelude::*;
#[derive(Clone, Routable, PartialEq)]
enum Route {
#[at("/")]
Home,
#[at("/secure")]
Secure,
#[not_found]
#[at("/404")]
NotFound,
}
Route 與 <Switch /> 元件配對,後者會找到與瀏覽器目前 URL 相符的路徑變體,並將其傳遞給 render 回呼。然後回調決定要渲染的內容。如果沒有路徑匹配,路由器會導航到帶有 not_found 屬性的路徑。如果沒有指定路由,則不會渲染任何內容,並且會在控制台中記錄一條訊息,說明沒有符合的路由。
yew-router 的大多數元件,特別是 <Link /> 和 <Switch />,必須是某個 Router 元件(例如 <BrowserRouter />)的(深層)子元素。通常在應用程式中只需要一個 Router,通常由最頂層的 <App /> 元件立即渲染。 Router 註冊了一個上下文,這是 Links 和 Switches 功能所需的。下面提供了一個範例。
在瀏覽器環境中使用 yew-router 時,強烈建議使用 <BrowserRouter />。您可以在 API 參考 中找到其他路由器類型。
use yew_router::prelude::*;
use yew::prelude::*;
#[derive(Clone, Routable, PartialEq)]
enum Route {
#[at("/")]
Home,
#[at("/secure")]
Secure,
#[not_found]
#[at("/404")]
NotFound,
}
#[component(Secure)]
fn secure() -> Html {
let navigator = use_navigator().unwrap();
let onclick = Callback::from(move |_| navigator.push(&Route::Home));
html! {
<div>
<h1>{ "Secure" }</h1>
<button {onclick}>{ "Go Home" }</button>
</div>
}
}
fn switch(routes: Route) -> Html {
match routes {
Route::Home => html! { <h1>{ "Home" }</h1> },
Route::Secure => html! {
<Secure />
},
Route::NotFound => html! { <h1>{ "404" }</h1> },
}
}
#[component(Main)]
fn app() -> Html {
html! {
<BrowserRouter>
<Switch<Route> render={switch} /> // <- must be child of <BrowserRouter>
</BrowserRouter>
}
}
路徑段
路由還可以使用動態和命名通配符段從路由中提取資訊。然後,您可以在 <Switch /> 內存取貼文的 id,並透過屬性將其轉發到對應的元件。
use yew::prelude::*;
use yew_router::prelude::*;
#[derive(Clone, Routable, PartialEq)]
enum Route {
#[at("/")]
Home,
#[at("/post/:id")]
Post { id: String },
#[at("/*path")]
Misc { path: String },
}
fn switch(route: Route) -> Html {
match route {
Route::Home => html! { <h1>{ "Home" }</h1> },
Route::Post { id } => html! {<p>{format!("You are looking at Post {}", id)}</p>},
Route::Misc { path } => html! {<p>{format!("Matched some other path: {}", path)}</p>},
}
}
您也可以使用普通的 Post 變體,而不是 Post {id: String}。例如,當 Post 與另一個路由器一起渲染時,該欄位可能是多餘的,因為另一個路由器可以匹配並處理路徑。有關詳細信息,請參閱下面的嵌套路由器部分。
請注意,欄位必須實作 Clone + PartialEq 作為 Route 枚舉的一部分。它們還必須實作 std::fmt::Display 和 std::str::FromStr 以進行序列化和反序列化。整數、浮點數和字串等原始類型已經滿足這些要求。
當路徑的形式匹配,但反序列化失敗(根據 FromStr)。路由器將認為路由不匹配,並嘗試渲染未找到的路由(或者如果未指定未找到的路由,則渲染空白頁面)。
參考以下範例:
#[derive(Clone, Routable, PartialEq)]
enum Route {
#[at("/news/:id")]
News { id: u8 },
#[not_found]
#[at("/404")]
NotFound,
}
// 切換函數會渲染 News 和 id。這裡省略了。
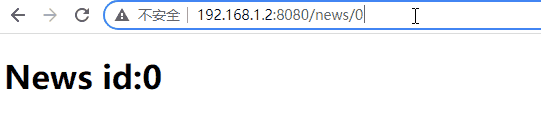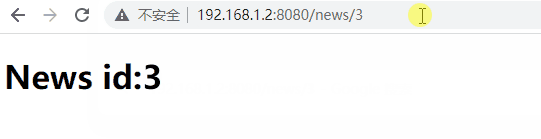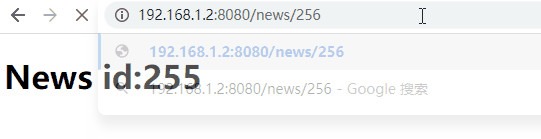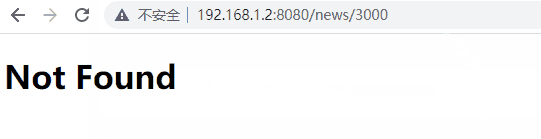
當段超過 255 時,u8::from_str() 將失敗並傳回 ParseIntError,路由器將認為路由不符。
有關路由語法和如何綁定參數的更多信息,請查看 route-recognizer。
位置 (Location)
路由器透過上下文提供了一個通用的 Location 結構,可以用來存取路由資訊。它們可以透過鉤子或 ctx.link() 上的便捷函數來檢索。
導航
yew_router 提供了一些工具來處理導航。
連結
<Link /> 渲染為<a> 元素,onclick 事件處理程序將呼叫 preventDefault,並將目標頁面推送到歷史記錄中並渲染所需的頁面,這正是單頁應用程式所期望的行為。普通錨元素的預設 onclick 會重新載入頁面。
<Link /> 元件也會將其子元素傳遞給 <a> 元素。可以將其視為應用程式內路由的 <a/> 替代品。不同之處在於你需要提供 to 屬性而不是 href。範例用法如下:
<Link<Route> to={Route::Home}>{ "click here to go home" }</Link<Route>>
結構體變數也可以正常運作:
<Link<Route> to={Route::Post { id: "new-yew-release".to_string() }}>{ "Yew!" }</Link<Route>>
導航接口
導航器 API 為函數元件和結構元件提供。它們使回調能夠更改路由。可以在任一情況下取得 Navigator 實例以操作路由。
函數式元件
對於函數元件,當底層導覽器提供者變更時,use_navigator 鉤子會重新渲染元件。
以下是實現一個按鈕的範例,該按鈕在點擊時導航到 Home 路由。
#[component(MyComponent)]
pub fn my_component() -> Html {
let navigator = use_navigator().unwrap();
let onclick = Callback::from(move |_| navigator.push(&Route::Home));
html! {
<>
<button {onclick}>{"Click to go home"}</button>
</>
}
}
這裡的範例使用了 Callback::from。如果目標路由可以與元件所在的路由相同,或只是為了安全起見,請使用普通的回呼。例如,考慮在每個頁面上都有一個徽標按鈕,點擊該按鈕會返回主頁。在主頁上點擊該按鈕兩次會導致程式碼崩潰,因為第二次點擊會推送一個相同的 Home 路由,並且 use_navigator 鉤子不會觸發重新渲染。
如果您想要取代目前的位置而不是將新位置推到堆疊上,請使用 navigator.replace() 而不是 navigator.push()。
您可能會注意到 navigator 必須移動到回呼中,因此不能再次用於其他回呼。幸運的是,navigator 實作了 Clone,例如,以下是如何為不同的路由設定多個按鈕:
use yew::prelude::*;
use yew_router::prelude::*;
#[component(NavItems)]
pub fn nav_items() -> Html {
let navigator = use_navigator().unwrap();
let go_home_button = {
let navigator = navigator.clone();
let onclick = Callback::from(move |_| navigator.push(&Route::Home));
html! {
<button {onclick}>{"click to go home"}</button>
}
};
let go_to_first_post_button = {
let navigator = navigator.clone();
let onclick = Callback::from(move |_| navigator.push(&Route::Post { id: "first-post".to_string() }));
html! {
<button {onclick}>{"click to go the first post"}</button>
}
};
let go_to_secure_button = {
let onclick = Callback::from(move |_| navigator.push(&Route::Secure));
html! {
<button {onclick}>{"click to go to secure"}</button>
}
};
html! {
<>
{go_home_button}
{go_to_first_post_button}
{go_to_secure_button}
</>
}
}
結構體組件
對於結構體元件,可以透過 ctx.link().navigator() API 取得 Navigator 實例。其餘部分與函數組件的情況相同。以下是一個渲染單一按鈕的視圖函數範例。
fn view(&self, ctx: &Context<Self>) -> Html {
let navigator = ctx.link().navigator().unwrap();
let onclick = Callback::from(move |_| navigator.push(&MainRoute::Home));
html!{
<button {onclick}>{"Go Home"}</button>
}
}
重定向
yew-router 在 prelude 中也提供了一個 <Redirect /> 元件。它可以用於實現與導航器 API 類似的效果。該元件接受一個 to 屬性作為目標路由。當渲染 <Redirect/> 時,使用者將被重定向到屬性中指定的路由。以下是一個範例:
#[component(SomePage)]
fn some_page() -> Html {
// 建立對 `use_user` 的鉤子
let user = match use_user() {
Some(user) => user,
// 當使用者為 `None` 時重定向到登入頁面
None => return html! {
<Redirect<Route> to={Route::Login}/>
},
};
// ... 實際頁面內容
}
Redirect 或 NavigatorNavigator API 是在回呼中操作路由的唯一方法。
而 <Redirect /> 可以作為元件中的回傳值使用。您可能還想在其他非元件上下文中使用 <Redirect />,例如在嵌套路由器的 switch 函數中。
監聽變化
函數式元件
您可以使用 use_location 和 use_route 鉤子。當提供的值發生變化時,您的元件將重新渲染。
結構體組件
為了回應路由變化,您可以將回呼閉包傳遞給 ctx.link() 的 add_location_listener() 方法。
一旦位置監聽器被刪除,它將被取消註冊。請確保將句柄儲存在元件狀態中。
fn create(ctx: &Context<Self>) -> Self {
let listener = ctx.link()
.add_location_listener(ctx.link().callback(
// 處理事件
))
.unwrap();
MyComponent {
_listener: listener
}
}
ctx.link().location() 和 ctx.link().route::<R>() 也可以用於一次性擷取位置和路由。
查詢參數
在導航時指定查詢參數
為了在導覽到新路由時指定查詢參數,可以使用 navigator.push_with_query 或 navigator.replace_with_query 函數。它使用 serde 將參數序列化為 URL 的查詢字串,因此任何實作了 Serialize 的類型都可以傳遞。最簡單的形式是包含字串對的 HashMap。
取得目前路由的查詢參數
location.query 用來取得查詢參數。它使用 serde 從 URL 的查詢字串中反序列化參數。
嵌套路由器
當應用程式變得更大時,嵌套路由器可能會很有用。考慮以下路由器結構:


嵌套的 SettingsRouter 處理所有以 /settings 開頭的 URL。此外,它會將未符合的 URL 重新導向到主 NotFound 路由。因此,/settings/gibberish 將會重新導向到 /404。
請注意,該介面仍在開發中,這樣寫的方式尚未最終確定
可以使用以下程式碼實作:
use yew::prelude::*;
use yew_router::prelude::*;
use gloo::utils::window;
use wasm_bindgen::UnwrapThrowExt;
#[derive(Clone, Routable, PartialEq)]
enum MainRoute {
#[at("/")]
Home,
#[at("/news")]
News,
#[at("/contact")]
Contact,
#[at("/settings")]
SettingsRoot,
#[at("/settings/*")]
Settings,
#[not_found]
#[at("/404")]
NotFound,
}
#[derive(Clone, Routable, PartialEq)]
enum SettingsRoute {
#[at("/settings")]
Profile,
#[at("/settings/friends")]
Friends,
#[at("/settings/theme")]
Theme,
#[not_found]
#[at("/settings/404")]
NotFound,
}
fn switch_main(route: MainRoute) -> Html {
match route {
MainRoute::Home => html! {<h1>{"Home"}</h1>},
MainRoute::News => html! {<h1>{"News"}</h1>},
MainRoute::Contact => html! {<h1>{"Contact"}</h1>},
MainRoute::SettingsRoot | MainRoute::Settings => html! { <Switch<SettingsRoute> render={switch_settings} /> },
MainRoute::NotFound => html! {<h1>{"Not Found"}</h1>},
}
}
fn switch_settings(route: SettingsRoute) -> Html {
match route {
SettingsRoute::Profile => html! {<h1>{"Profile"}</h1>},
SettingsRoute::Friends => html! {<h1>{"Friends"}</h1>},
SettingsRoute::Theme => html! {<h1>{"Theme"}</h1>},
SettingsRoute::NotFound => html! {<Redirect<MainRoute> to={MainRoute::NotFound}/>}
}
}
#[component(App)]
pub fn app() -> Html {
html! {
<BrowserRouter>
<Switch<MainRoute> render={switch_main} />
</BrowserRouter>
}
}
基底路徑 (Basename)
可以使用 yew-router 定義基底路徑 (Basename)。
基底路徑是所有路由的公共前綴。導航器 API 和 <Switch /> 元件都支援基底路徑設定。所有推送的路由都會加上基底路徑前綴,所有的 switch 都會在嘗試將路徑解析為 Routable 之前去掉基底路徑。
如果沒有為 Router 元件提供基底路徑屬性,它將使用 HTML 檔案中 <base /> 元素的 href 屬性,並在 HTML 檔案中沒有 <base /> 元素時回退到 /。